Xinquan Wang’s group published an article in PNAS, revealing the structural basis for the interaction of interleukin- 33 with its receptors
On Aug 26th 2013, a joint team led by Dr. Xinquan Wang in Tsinghua University and Dr. Shuying Wang in National Cheng Kung University published an article in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS), reporting their latest results in the structural study of interleukin- 33 (IL-33) with its receptor.
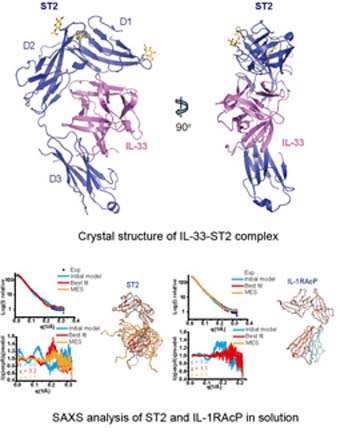
IL-33 is the latest member of IL-1 cytokine family that has pleiotropic activities in innate and adaptive immune responses in host defense and disease. The biological function of IL-33 is mediated by its specific receptor ST2 and co-receptor IL-1RAcP on the target cell membrane. The authors determined the crystal structure of mature IL-33 (amino acid residues 112-270) complexed with the extracellular domain of ST2 receptor. Coupled with structure-based mutagenesis and binding assay, the structural results define the molecular mechanism by which ST2 specifically recognizes IL-33. Structural comparison with other ligand-receptor complexes in the IL-1 family indicates that surface charge complementarity is critical in determining ligand-binding specificity of IL-1 primary receptors. Combined crystallography and small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) studies reveal that ST2 possesses hinge flexibility between the D3 domain and D1D2 module, while IL-1RAcP exhibits a rigid conformation in the unbound state in solution. The molecular flexibility of ST2 provides structural insights into domain-level conformational change of IL-1 primary receptors upon ligand binding, and the rigidity of IL-1RAcP explains its inability to bind ligands directly. The solution architecture of IL-33-ST2-IL-1RAcP complex from SAXS analysis resembles IL-1β-IL-1RII-IL-1RAcP and IL-1β-IL-1RI-IL-1RAcP crystal structures. The collective results confer IL-33 structure-function relationships, supporting and extending a general model for ligand-receptor assembly and activation in the IL-1 family proposed in their Nature Immunology paper published in 2010.
Drs. Xinquan Wang and Shuying Wang are the corresponding authors of this article. Ph.D. student Xi Liu in the School of Life Sciences, Tsinghua University is the first author of this publication. Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (SSRF) and Berkeley ALS synchrotron radiation source provided support for data collection.

